SUMMARY: The FDA on September 21, 2022, granted accelerated approval to Selpercatinib (RETEVMO®) for adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors with a Rearranged during Transfection (RET) gene fusion that have progressed on or following prior systemic treatment, or who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options. The FDA on the same day also granted Regular approval to Selpercatinib for adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with a Rearranged during Transfection (RET) gene fusion, as detected by an FDA-approved test. FDA also approved the Oncomine Dx Target (ODxT) Test as a companion diagnostic for Selpercatinib.
In addition to the well characterized gene fusions involving ALK and ROS1 in NSCLC, genetic alterations involving other kinases including EGFR, BRAF, RET, NTRK, are all additional established targetable drivers. These genetic alterations are generally mutually exclusive, with no more than one predominant driver in any given cancer. The hallmark of all these genetic alterations is oncogene addiction, in which cancers are driven primarily, or even exclusively, by aberrant oncogene signaling, and are highly susceptible to small molecule inhibitors.
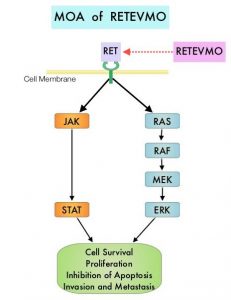
RET kinase is a transmembrane Receptor Tyrosine Kinase and plays an important role during the development and maintenance of a variety of tissues, including neural and genitourinary tissues. RET signaling activates downstream pathways such as JAK/STAT3 and RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and leads to cellular proliferation, survival, invasion, and metastasis. Oncogenic alterations to the RET proto-oncogene result in uncontrolled cell growth and enhanced tumor invasiveness. RET alterations include RET rearrangements, leading to RET fusions, and activating point mutations occurring across multiple tumor types. RET fusions have been identified in approximately 2% of NSCLCs, 10-20% of non-medullary thyroid cancers. Activating RET point mutations account for approximately 60% of sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancers (MTC) and more than 90% of inherited MTCs. Other cancers with documented RET alterations include colorectal, pancreas, breast, and several hematologic malignancies.
Selpercatinib is a highly selective and potent, oral anti-RET Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) designed to inhibit native RET signaling, as well as anticipated acquired resistance mechanisms. Selpercatinib selectively targets wild-type RET as well as various RET mutants and RET-containing fusion products. Additionally, Selpercatinib inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 (VEGFR1), VEGFR3, Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 (FGFR1), FGFR2, and FGFR3. This results in inhibition of cell growth of tumors that exhibit increased RET activity.
The LIBRETTO-001 is the largest open-label, multicenter, Phase I/II trial in patients with advanced solid tumors, including RET fusion-positive solid tumors, RET-mutant Medullary Thyroid Cancers, and other tumors with RET activation, treated with a RET inhibitor. To investigate the efficacy of Selpercatinib, the trial was conducted in 2 parts: Phase 1 (dose escalation) and Phase II (dose expansion). Patients with advanced cancer were eligible, if they have progressed on or were intolerant to available standard therapies, or no standard or available curative therapy existed, or in the opinion of the Investigator, they would be unlikely to tolerate or derive significant clinical benefit from appropriate standard of care therapy, or they declined standard therapy. A dose of 160 mg BID was the recommended Phase II dose. Up to about 850 patients with advanced solid tumors harboring a RET gene alteration in tumor and/or blood were enrolled in 6 different Phase II cohorts, based on tumor type, RET alteration and prior therapy. Identification of RET gene alterations were prospectively determined in local laboratories using either Next Generation Sequencing, Polymerase Chain Reaction, or Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization. The Phase II portion of the trial had a Primary endpoint of Objective Response Rate (ORR) by Blinded Independent Review Committee (BIRC) and Secondary endpoints of Duration of Response, CNS Objective Response Rate, Progression Free Survival (PFS) and safety.
RET Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors
This group included 41 patients and the most common cancers were pancreatic adenocarcinoma (27%), colorectal (24%), salivary (10%), and unknown primary (7%). Majority of the patients (90%) received 2 prior systemic therapies and 32% had received 3 or more. The median age of patients was 50 years, 54% were female, 68% were White, 24% were Asian, and 95% had metastatic disease. RET fusion-positive status was detected in 98% of patients using NGS and 2% using FISH.
The Objective Response Rate was 44%, with 5% Complete Response and 39% Partial Response. The median Duration of response was 24.5 months and 67% of patients had a Duration of Response of 6 months or more.
The NSCLC Cohort
Selpercatinib was previously granted accelerated approval in May 2020 for patients with metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC based on initial Overall Response Rate (ORR) and Duration of Response (DOR) among 144 patients enrolled in the LIBRETTO-001 trial. The conversion to regular and traditional FDA approval was based on data from an additional 172 patients and 18 months of additional follow up, to assess durability of response. Patients received Selpercatinib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity and efficacy was evaluated in a total of 316 patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC. The median age of patients was 61 years, 58% were female, 49% were White, 41% were Asian and 97% had metastatic disease. Previously treated patients received a median of two prior systemic therapies and 58% had received prior anti PD 1/PD-L1 therapy.
Among the 69 treatment-naïve patients, the ORR was 84%, with 6% Complete Response and 78% Partial Response. The median Duration of Response was 20.2 months and 50% of patients had a Duration of Response of 12 months or more. Among the 247 previously treated patients, the ORR was 61%, with 7% Complete Response and 54% Partial Response. The median Duration of Response was 28.6 months and 63% of patients had a Duration of Response of 12 months or more.
It is estimated that up to 50% of RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients can have brain metastases, and in the subset of patients with brain metastases (N=21), treatment with Selpercatinib demonstrated a CNS Objective Response Rate of 85%, and 38% of responders had an intracranial Duration of Response of 12 months or greater. The most common toxicities in patients were edema, diarrhea, fatigue, dry mouth, hypertension, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, nausea, and headache.
LIBRETTO-001 is the largest trial ever reported in RET-altered cancer patients and represents an important milestone in the Precision Medicine arena. Selpercatinib is the first and only RET inhibitor to receive both tumor-agnostic accelerated approval and traditional approval in NSCLC, reinforcing its benefits across diverse tumor types.
Selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion–positive non–small-cell lung cancer: updated safety and efficacy from the registrational libretto-001 phase I/II trial.Published September 19, 2022. Drilon A, Subbiah V, Gautschi O, et al. J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1200/JCO.22.00393
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-selpercatinib-locally-advanced-or-metastatic-ret-fusion-positive-solid-tumors