The FDA on January 19, 2024, approved BALVERSA® for adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma (mUC) with susceptible FGFR3 genetic alterations, as determined by an FDA-approved companion diagnostic test, whose disease has progressed on or after at least one line of prior systemic therapy. BALVERSA® is not recommended for the treatment of patients who are eligible for and have not received prior PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor therapy. This approval amends the indication previously granted under accelerated approval for patients with mUC with susceptible FGFR3 or FGFR2 alterations after prior platinum-containing chemotherapy. BALVERSA® is a product of Janssen Biotech.
Tag: Urothelial Cancer (Bladder-Ureters-Renal-Pelvis)
PADCEV® (Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv)
The FDA on December 15, 2023, approved PADCEV® in combination with Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA®) for patients with locally advanced or metastatic Urothelial Cancer. FDA previously granted accelerated approval to this combination for patients with locally advanced or metastatic Urothelial Cancer, who are ineligible for Cisplatin-containing chemotherapy. PADCEV® is a product of Astellas Pharma.
PADCEV® (Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv) with KEYTRUDA® (Pembrolizumab)
The FDA on April 3, 2023, granted accelerated approval to PADCEV® with KEYTRUDA® for patients with locally advanced or metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma who are ineligible for Cisplatin-containing chemotherapy. PADCEV® is a product of Astellas Pharma and KEYTRUDA® is a product of Merck.
FDA Approves Enfortumab vedotin with Pembrolizumab for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma
SUMMARY: The FDA on April 3, 2023, granted accelerated approval to Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv (PADCEV®) with Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA®) for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who are ineligible for Cisplatin-containing chemotherapy. The American Cancer Society estimates that in the United States for 2023, about 82,290 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed and approximately 16,710 patients will die of the disease. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men, but it is less common in women. Urothelial cancer accounts for 90% of all bladder cancers and can also be found in the renal pelvis, ureter and urethra. Approximately 12% of urothelial cancer cases at diagnosis are locally advanced or metastatic.
Patients with urothelial carcinoma are currently treated in the first line setting with a Platinum based chemotherapy regimen, and a checkpoint Inhibitor (PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor) in the second line setting. However, approximately 50% of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma are ineligible for Cisplatin-based chemotherapy due to toxicities, and responses are rarely durable. There is therefore a critical need for effective and tolerable first line treatment options in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv (PADCEV®) is a first-in-class Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) that targets Nectin-4, a cell adhesion molecule highly expressed in urothelial cancers and other solid tumors. Nectin-4 has been implicated in tumor cell growth and proliferation. Following binding to Nectin-4 on the cell surface, Enfortumab vedotin becomes internalized and is processed by lysosomes, with the liberation of its cytotoxic payload, MonoMethyl Auristatin E (MMAE), which in turn disrupts microtubule assembly, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Enfortumab vedotin resulted in significantly longer Overall Survival, Progression Free Survival, and a higher Overall Response Rate, than standard chemotherapy, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, who had previously received Platinum-based treatment and a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor. Preclinical studies with Enfortumab vedotin have shown hallmarks of immune cell death potentially augmented by PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and the rationale for this clinical trial was based on results from a previous cohort study.
Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA®) is a fully humanized, Immunoglobulin G4, anti-PD-1, monoclonal antibody, that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. By doing so, it unleashes the tumor-specific effector T cells, and is thereby able to undo PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response. Pembrolizumab is the first agent to improve Overall Survival over chemotherapy, in the second line setting, for patients with recurrent, advanced urothelial carcinoma, and a significant proportion of patients who respond, have very durable responses.
EV-103 is an ongoing multi-cohort, open-label, global, multicenter Phase Ib/II study, investigating Enfortumab vedotin alone or in combination with Pembrolizumab and/or chemotherapy in first or second line settings, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer, and in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The present FDA approval was based on Objective Response Rates (ORR) and median Duration of Response (DOR) in combined Dose Escalation/Cohort A and Cohort K of this study, also known as KEYNOTE-869 trial. The Dose Escalation Cohort and Cohort A were single-arm cohorts treating patients with Enfortumab vedotin plus Pembrolizumab, whereas patients in Cohort K were randomized to either Enfortumab vedotin monotherapy or Enfortumab vedotin in combination with Pembrolizumab. Patients had not received prior systemic therapy for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer and were ineligible for Cisplatin-containing chemotherapy. Ineligibility for Cisplatin-based chemotherapy could be due to at least one of the following: Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) less than 60 mL/min, ECOG Performance Status of 2, Grade 2 or more hearing loss, or New York Heart Association Class III heart failure. In this analysis, a total of 121 patients (N=121) received Enfortumab vedotin plus Pembrolizumab. Patients received Enfortumab vedotin 1.25 mg/kg IV (up to a maximum of 125 mg for patients 100 kg or more) on days 1 and 8 and Pembrolizumab 200 mg IV on day 1, every 3 weeks. Treatment was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measures were Objective Response Rate (ORR) and Duration of Response (DOR) determined by Blinded Independent Central Review.
Patients treated with a combination of Enfortumab vedotin and Pembrolizumab had an Objective Response Rate of 68%, with 12% of patients experiencing a Complete Response. The median Duration of Response for the Dose Escalation cohort plus Cohort A was 22 months and for Cohort K was Not Reached. The most common Treatment Related Adverse Events (TRAE) were peripheral sensory neuropathy (55.6%), fatigue (51.1%), and alopecia (48.9%). Two thirds of patients had Grade 3 TRAEs, and the most common toxicities were increased lipase, maculopapular rash, and fatigue.
It was concluded that in Cisplatin-ineligible patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer, treatment with Enfortumab vedotin and Pembrolizumab combination in chemo naïve patients, resulted in high Overall Response Rate, along with a safety profile that was tolerable. The authors added that Antibody-Drug Conjugates have the potential to make a greater impact in treating bladder cancer, especially in combination with checkpoint inhibitors, as shown in this trial and these data support ongoing investigations of first line Enfortumab vedotin and Pembrolizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer.
Enfortumab Vedotin Plus Pembrolizumab in Previously Untreated Advanced Urothelial Cancer. Hoimes CJ, Flaig TW, Milowsky M, et al. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.01643 Journal of Clinical Oncology 41, no. 1 (January 01, 2023) 22-31.
Biomarkers May Predict Response to Enfortumab Vedotin in Advanced Urothelial Cancer
SUMMARY: The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2023, approximately 82,290 new cases of Bladder Cancer will be diagnosed and 16,710 patients will die of the disease. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men, but it is less common in women. A third of the patients initially present with locally invasive or metastatic disease. Patients with urothelial carcinoma are currently treated in the first line setting with a Platinum based chemotherapy regimen and a checkpoint Inhibitor (PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor) in the second line setting. Treatment options for patients who progress after first and second line therapies are limited, with poor outcomes. The response rates with standard chemotherapy in this patient population, is about 10%. Approximately 50% of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma are ineligible for Cisplatin-based chemotherapy. There is therefore a critical need for effective and tolerable first line treatment options in locally advanced or metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma.
Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv (PADCEV®) is an Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) that targets Nectin-4, a cell adhesion molecule highly expressed in urothelial cancers and other solid tumors. Nectin-4 has been implicated in tumor cell growth and proliferation. Following binding to Nectin-4 on the cell surface, Enfortumab vedotin becomes internalized and is processed by lysosomes, with the liberation of its cytotoxic payload, Monomethyl auristatin E, which in turn disrupts microtubule assembly, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Enfortumab vedotin resulted in significantly longer Overall Survival, Progression Free Survival, and a higher Overall Response Rate, than standard chemotherapy, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, who had previously received Platinum-based treatment and a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor. However there are limited data available on biomarkers predictive of outcomes when treated with Enfortumab vedotin.
The researchers in this study investigated potential biomarkers of response to Enfortumab vedotin by analyzing data from the UNITE (Urothelial Cancer Network to Investigate Therapeutic Experiences) database. This analysis include 170 patients from 16 different sites, with available Next Generation Sequencing using institutional or commercial platforms, treated with Enfortumab vedotin alone, outside of a clinical trial setting, for whom outcomes were available. The median age was 70 years, 78% were men, 65% had pure urothelial histology, 69% had primary bladder tumor, and 68% had 2 or more lines of therapy before Enfortumab vedotin.
The following molecular biomarkers were assessed: Tumor Mutation Burden (TMB), PD-L1 status, presence of 1 or more DNA damage response mutations such as BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, ATM, CHEK2, CDK12, BARD1, PPP2R2A, or RAD51B, and somatic alterations such as TERTp, TP53, ARID1A, CDKN2A, CDKN2B, FGFR3, ERBB2, CCND1, KDM6A, MTAP, PIK3CA, RB1, TSC1, in 10% or more of patients. Investigators determined observed response to Enfortumab vedotin in patients with scans after one or more doses of the therapy.
For all patients included in this analysis, the Observed Response Rate was 47%, median Progression Free Survival was 6 months and median Overall Survival was 12 months. The Observed Response Rates were higher in patients with ERBB2 and TSC1 alterations versus wild-type (67% versus 44%; P=0.05 and 68% versus 25%; P=0.04, respectively). Shorter median Progression Free Survival was noted in patients with CDKN2A, CDKN2B, and MTAP alterations, whereas patients with high Tumor Mutation Burden (10 or more Mut/Mb) had longer median Overall Survival.
It was concluded that analysis of this large, multicenter, retrospective cohort of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma, identified several potential biomarkers associated with differential outcomes to Enfortumab vedotin, and these findings may help inform clinical decision making and potential therapy sequencing.
Biomarkers of response to enfortumab vedotin (EV) in patients (pts) with advanced urothelial carcinoma (aUC): Analysis of the UNITE study. Jindal T, Kilari D, Alhalabi O, et al.DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2023.41.6_suppl.450 Journal of Clinical Oncology.
FDA Approves First Gene Therapy for Bladder Cancer
SUMMARY: The FDA on December 16, 2022, approved ADSTILADRIN® (Nadofaragene firadenovec-vncg) for adult patients with high-risk Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) unresponsive Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) with Carcinoma in Situ (CIS) with or without papillary tumors. According to the American Cancer Society, 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer were diagnosed in 2022 and 17,100 died of the disease. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men but is less common in women and the average age at the time of diagnosis is 73 years. With regards to racial predisposition, Caucasians are more likely to be diagnosed with bladder cancer than African Americans or Hispanic Americans.
Approximately 50% of all bladder cancers are non-invasive or in situ cancers. The current standard intervention for superficial bladder cancers-Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) involves removing the bladder tumor and intravesical treatment with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) immunotherapy, for patients with high-risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer, including those with Carcinoma in Situ, High Grade T1, or large-volume or recurrent Ta tumors, to reduce the risk of recurrence. Although 80% of patients have an initial complete response to BCG, more than half of patients have recurrence and progression within the first year, and develop resistance to BCG. These patients are often given the treatment option of radical cystectomy, which includes removing the entire urinary bladder and a prostatectomy for men or total hysterectomy in women. While highly curative, this surgical procedure carries substantial risk for morbidity and mortality, and can negatively impact patient’s quality of life. Further, a significant proportion of patients are medically ineligible for a radical cystectomy, and even if eligible, refuse surgery and opt for other less effective treatments, which could compromise outcomes. The development of a safe, effective and durable intravesical treatment remains a critical unmet need for patients who want to avoid radical cystectomy or systemic immunotherapy.
ADSTILADRIN® (Nadofaragene firadenovec-vncg) is a nonreplicating recombinant adenovirus vector-based gene therapy, that delivers a copy of the human Interferon alfa-2b gene to the patient’s bladder urothelial cells. This novel gene therapy approach provides a longer duration of exposure of the urothelium to Interferon alfa-2b, by allowing the urothelial cells to produce Interferon on an ongoing basis. The safety and efficacy of intravesical ADSTILADRIN® for patients with BCG-refractory and relapsing non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer, was demonstrated in Phase I and Phase II clinical trials. The present study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intravesical ADSTILADRIN® in a larger population of patients with BCG-unresponsive Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer.
This Phase III multicenter, open-label, single-arm trial enrolled 157 patients with high-risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer, 98 of whom had BCG-unresponsive Carcinoma in Situ, evaluable for response. A single-arm design was adopted as there is no standard treatment for this patient population. BCG-unresponsive high-risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) was defined as persistent disease despite adequate BCG therapy, disease recurrence after an initial tumor-free state following adequate BCG therapy, or T1 disease following BCG. Patients received ADSTILADRIN® 75 mL intravesical instillation (3 x 1011 viral particles/mL) once every three months up to 12 months, unacceptable toxicity, or recurrent high-grade NMIBC. Patients without high-grade recurrence were allowed to continue ADSTILADRIN® every three months. The major efficacy outcome measures were Complete Response (CR) at any time and Duration of Response (DoR). CR was defined as negative cystoscopy with applicable TransUrethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT) and biopsies, and urine cytology. Random bladder biopsies of five sites were conducted in patients remaining in CR at 12 months.
The Complete Response Rate was 51%, the median Duration of Response was 9.7 months and 46% of responding patients remained in Complete Response for at least one year. The most common grade 3 adverse reaction was micturition urgency (1%). Most of patients experienced Grade 1 Adverse Events which included mild fatigue and bladder spasms. The most common Grade 3 toxicity was urinary urgency noted in 1% of patients.
This study has demonstrated that Intravesical delivery of the adenoviral vector containing the human recombinant Interferon alfa-2b gene was associated with promising efficacy outcomes, with an acceptable safety profile. ADSTILADRIN® is a novel treatment option and alternative to chemotherapy and systemic therapies and is the first FDA-approved gene therapy for bladder cancer.
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-first-adenoviral-vector-based-gene-therapy-high-risk-bacillus-calmette-guerin
ADSTILADRIN® (Nadofaragene firadenovec-vncg)
The FDA on December 16, 2022, approved ADSTILADRIN® (Nadofaragene firadenovec-vncg) for adult patients with high-risk Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) unresponsive Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) with Carcinoma in Situ (CIS), with or without papillary tumors. ADSTILADRIN® is a product of Ferring Pharmaceuticals.
OPDIVO® (nivolumab) for the Adjuvant Treatment of High-Risk Urothelial Carcinoma*
*Urothelial carcinoma at high risk of recurrence after undergoing radical resection.
Written by: Terence Friedlander, MD
Professor of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Oncology, Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California, San Francisco
Content sponsored by: Bristol Myers Squibb
Dr Friedlander is a paid consultant for BMS and was compensated for his contribution in drafting this content.
Overview of High-Risk Urothelial Carcinoma*
Currently, radical resection with or without perioperative therapy is the standard of care for treating high-risk urothelial carcinoma (UC).1* However, there is still a high chance of recurrence within 2 years of radical resection, with less favorable survival rates for the high-risk patient population.1 While neoadjuvant therapy has an established role in treating high-risk UC,* data are less clear regarding the role of adjuvant therapy.2 In a retrospective observational cohort study of patients 65 years or older with UC at high risk of recurrence after radical resection, including patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, median disease-free survival (mDFS) was determined to be 13.5 months.1 Cisplatin-based chemotherapy is the neoadjuvant standard of care, but prior to 2021 there were no FDA-approved adjuvant therapy options.1-3 Studies have shown that adjuvant chemotherapy may delay recurrence and improve overall survival (OS), but these studies have not definitively shown a survival benefit, largely due to inadequate sample sizes.2 Additionally, approximately 50% of patients are ineligible for cisplatin-based treatment.1 As a result, there is a high unmet need for this difficult-to-treat population, and it is important for the urologist, oncologist, and patient to discuss and align on perioperative treatments at the time of diagnosis and early in the patient journey.1,2,4 Entering the adjuvant treatment landscape, immune checkpoint inhibitors may be an additional treatment option for HCPs to consider for their patients with high-risk UC.1,2*
Adjuvant OPDIVO in High-Risk Urothelial Carcinoma*
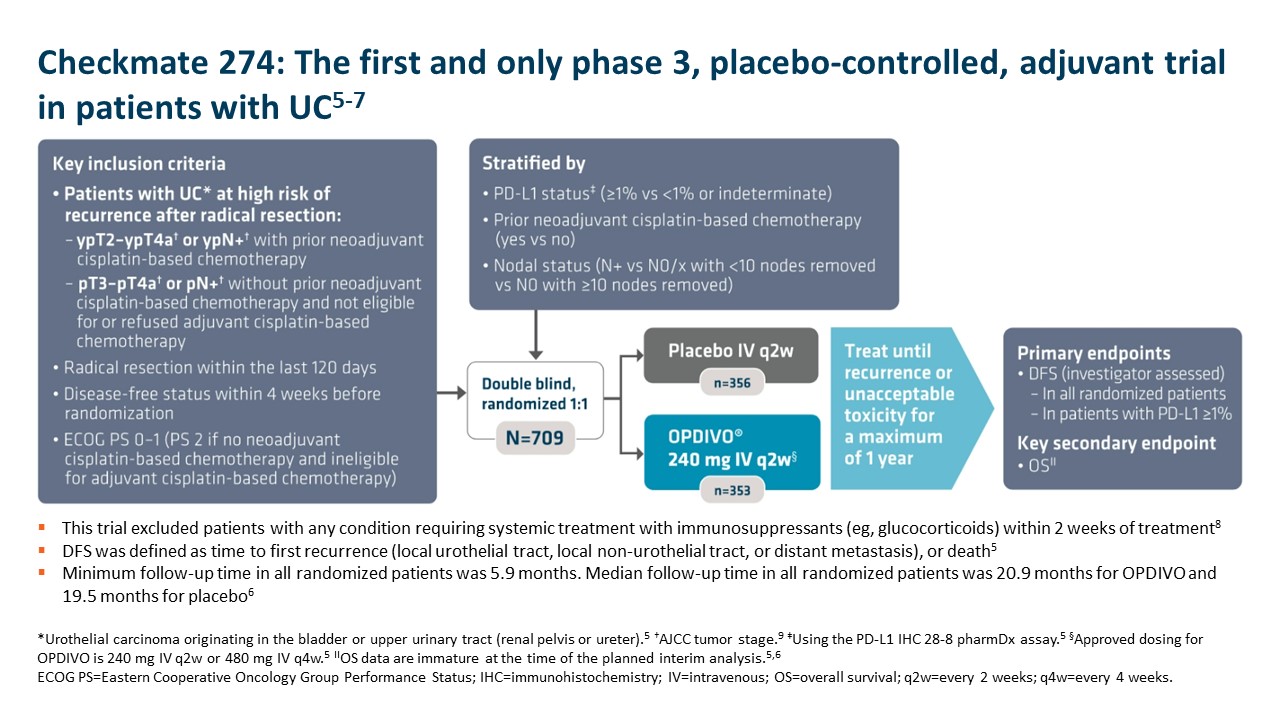
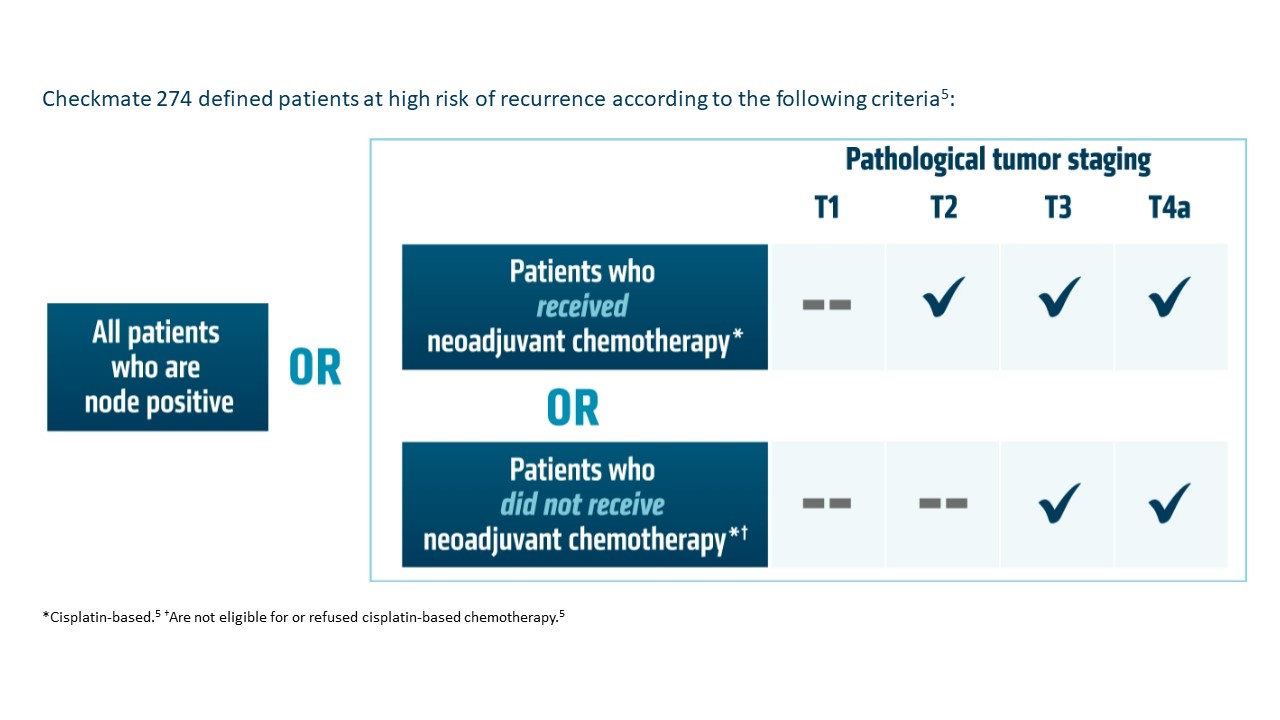
OPDIVO is approved and indicated for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with UC who are at high risk of recurrence after undergoing radical resection, regardless of prior neoadjuvant chemotherapy, nodal involvement, or PD-L1 status.5 The approval is based on Checkmate 274, a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized trial of adjuvant OPDIVO versus placebo.6 More information on the study design can be found in the images below. Baseline characteristics were balanced across treatment arms.6
 Important Safety Information
Important Safety Information
Select Important Safety Information
In Checkmate 274, serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of OPDIVO patients. The most frequent serious adverse reaction reported in ≥2% of patients was urinary tract infection. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1% of patients; these included events of pneumonitis (0.6%). The most-common adverse reactions reported in ≥20% of patients were rash, fatigue, diarrhea, pruritus, musculoskeletal pain, and UTI. OPDIVO was discontinued or delayed due to adverse reactions in 18% and 33% of patients, respectively.5
OPDIVO is associated with the following Warnings and Precautions: severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis and hepatotoxicity, endocrinopathies, nephritis with renal dysfunction, dermatologic adverse reactions, other immune-mediated adverse reactions; infusion-related reactions; complications of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; embryo-fetal toxicity; and increased mortality in patients with multiple myeloma when OPDIVO is added to a thalidomide analogue and dexamethasone, which is not recommended outside of controlled clinical trials.
OPDIVO may cause severe infusion-related reactions. In patients who received OPDIVO as a 60-minute intravenous infusion, infusion-related reactions occurred in 6.4% (127/1994) of patients.5 For additional information regarding infusion-related reactions, please see Important Safety Information for OPDIVO.
 Checkmate 274 was not powered to detect differences in the treatment effect at extended follow-up analysis; therefore, results from this exploratory analysis should be interpreted with caution.
Checkmate 274 was not powered to detect differences in the treatment effect at extended follow-up analysis; therefore, results from this exploratory analysis should be interpreted with caution.
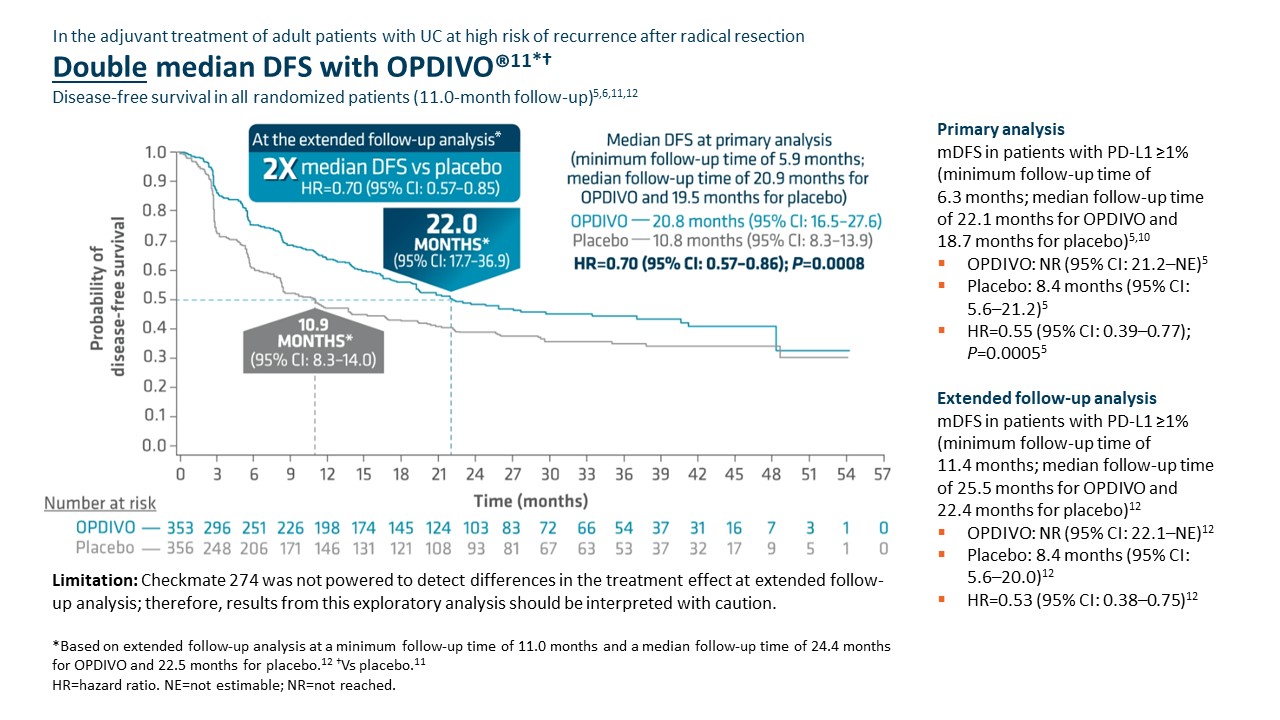
Adjuvant OPDIVO demonstrated superior disease-free survival (DFS) compared with placebo at the primary analysis (minimum follow-up of 5.9 months).5,6 Median DFS was 20.8 months with OPDIVO versus 10.8 months with placebo (HR=0.70 [95% CI: 0.57–0.86];P=0.0008).5 OS was also evaluated as a secondary endpoint, but at the time of the planned interim analysis, these data were immature with 33% of deaths in the ITT population; in the UTUC subpopulation, 37 deaths occurred, 20 of which occurred with OPDIVO versus 17 with placebo.5 Although the subgroup analyses were not statistically powered, for patients with prior neoadjuvant cisplatin therapy (n=308), the DFS hazard ratio was 0.52 [95% CI: 0.38–0.71] and for patients without prior neoadjuvant cisplatin therapy (n=401), the DFS hazard ratio was 0.92 [95% CI: 0.69–1.21].6 In additional exploratory subgroup analyses, no improvement in DFS was observed with nivolumab compared to placebo in patients with UTUC (n=149) the unstratified DFS hazard ratio was 1.15 (95% CI: 0.74–1.80); in patients with PD-L1 expression of <1% (n=414), the unstratified DFS hazard ratio was 0.83 (95% CI: 0.64–1.08).5
At the extended follow-up analysis (minimum follow-up of 11.0 months), mDFS was doubled with adjuvant OPDIVO compared with placebo. Median DFS was 22.0 months with OPDIVO versus 10.9 months with placebo (HR=0.70 [95% CI: 0.57–0.85]).12
Summary/conclusions
Given the high unmet need in this difficult-to-treat population, the call for approved adjuvant treatment options continues to rise.1,2 Adjuvant OPDIVO offers a chance to change the future for patients with high-risk UC as the only FDA-approved adjuvant option for adult patients with UC at high risk of recurrence after radical resection regardless of prior neoadjuvant chemotherapy, nodal involvement, or PD-L1 status.5,6,12 In Checkmate 274, OPDIVO significantly extended mDFS at the time of primary analysis and doubled mDFS at the time of extended follow-up analysis.5,6,12 Further data will be generated for the secondary endpoint of OS, which may provide greater insight into the efficacy of OPDIVO in this context.6,8 Given the clinical profile of Checkmate 274 and subsequent FDA approval, OPDIVO may help extend DFS for appropriate patients in need of treatment in the adjuvant UC setting.5,6,12
*Urothelial carcinoma at high risk of recurrence after undergoing radical resection.
Additional Definitions
CI=confidence interval; HCP=healthcare provider; HR=hazard ratio; ITT=intent to treat; PD-L1=programmed death ligand 1; UTUC=upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
Indication
OPDIVO® (nivolumab), as a single agent, is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with urothelial carcinoma (UC) who are at high risk of recurrence after undergoing radical resection of UC.
Important Safety Information
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-mediated adverse reactions listed herein may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue. While immune-mediated adverse reactions usually manifest during treatment, they can also occur after discontinuation of OPDIVO. Early identification and management are essential to ensure safe use of OPDIVO. Monitor for signs and symptoms that may be clinical manifestations of underlying immune-mediated adverse reactions. Evaluate clinical chemistries including liver enzymes, creatinine, and thyroid function at baseline and periodically during treatment with OPDIVO. In cases of suspected immune-mediated adverse reactions, initiate appropriate workup to exclude alternative etiologies, including infection. Institute medical management promptly, including specialty consultation as appropriate.
Withhold or permanently discontinue OPDIVO depending on severity (please see section 2 Dosage and Administration in the accompanying Full Prescribing Information). In general, if OPDIVO interruption or discontinuation is required, administer systemic corticosteroid therapy (1 to 2 mg/kg/day prednisone or equivalent) until improvement to Grade 1 or less. Upon improvement to Grade 1 or less, initiate corticosteroid taper and continue to taper over at least 1 month. Consider administration of other systemic immunosuppressants in patients whose immune-mediated adverse reactions are not controlled with corticosteroid therapy. Toxicity management guidelines for adverse reactions that do not necessarily require systemic steroids (e.g., endocrinopathies and dermatologic reactions) are discussed below.
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
OPDIVO can cause immune-mediated pneumonitis. The incidence of pneumonitis is higher in patients who have received prior thoracic radiation. In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 3.1% (61/1994) of patients, including Grade 4 (<0.1%), Grade 3 (0.9%), and Grade 2 (2.1%).
Immune-Mediated Colitis
OPDIVO can cause immune-mediated colitis. A common symptom included in the definition of colitis was diarrhea. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection/reactivation has been reported in patients with corticosteroid-refractory immune-mediated colitis. In cases of corticosteroid-refractory colitis, consider repeating infectious workup to exclude alternative etiologies. In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, immune-mediated colitis occurred in 2.9% (58/1994) of patients, including Grade 3 (1.7%) and Grade 2 (1%).
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis and Hepatotoxicity
OPDIVO can cause immune-mediated hepatitis. In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, immune-mediated hepatitis occurred in 1.8% (35/1994) of patients, including Grade 4 (0.2%), Grade 3 (1.3%), and Grade 2 (0.4%).
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
OPDIVO can cause primary or secondary adrenal insufficiency, immune-mediated hypophysitis, immune- mediated thyroid disorders, and Type 1 diabetes mellitus, which can present with diabetic ketoacidosis. Withhold OPDIVO depending on severity (please see section 2 Dosage and Administration in the accompanying Full Prescribing Information). For Grade 2 or higher adrenal insufficiency, initiate symptomatic treatment, including hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Hypophysitis can present with acute symptoms associated with mass effect such as headache, photophobia, or visual field defects. Hypophysitis can cause hypopituitarism; initiate hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Thyroiditis can present with or without endocrinopathy. Hypothyroidism can follow hyperthyroidism; initiate hormone replacement or medical management as clinically indicated. Monitor patients for hyperglycemia or other signs and symptoms of diabetes; initiate treatment with insulin as clinically indicated.
In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, adrenal insufficiency occurred in 1% (20/1994), including Grade 3 (0.4%) and Grade 2 (0.6%).
In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, hypophysitis occurred in 0.6% (12/1994) of patients, including Grade 3 (0.2%) and Grade 2 (0.3%).
In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, thyroiditis occurred in 0.6% (12/1994) of patients, including Grade 2 (0.2%).
In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, hyperthyroidism occurred in 2.7% (54/1994) of patients, including Grade 3 (<0.1%) and Grade 2 (1.2%).
In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, hypothyroidism occurred in 8% (163/1994) of patients, including Grade 3 (0.2%) and Grade 2 (4.8%).
In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, diabetes occurred in 0.9% (17/1994) of patients, including Grade 3 (0.4%) and Grade 2 (0.3%), and 2 cases of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Immune-Mediated Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction
OPDIVO can cause immune-mediated nephritis. In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, immune-mediated nephritis and renal dysfunction occurred in 1.2% (23/1994) of patients, including Grade 4 (<0.1%), Grade 3 (0.5%), and Grade 2 (0.6%).
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
OPDIVO can cause immune-mediated rash or dermatitis. Exfoliative dermatitis, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) has occurred with PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies. Topical emollients and/or topical corticosteroids may be adequate to treat mild to moderate nonexfoliative rashes.
Withhold or permanently discontinue OPDIVO depending on severity (please see section 2 Dosage and Administration in the accompanying Full Prescribing Information).
In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy, immune-mediated rash occurred in 9% (171/1994) of patients, including Grade 3 (1.1%) and Grade 2 (2.2%).
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
The following clinically significant immune-mediated adverse reactions occurred at an incidence of <1% (unless otherwise noted) in patients who received OPDIVO monotherapy or were reported with the use of other PD-1/PD- L1 blocking antibodies. Severe or fatal cases have been reported for some of these adverse reactions: cardiac/vascular: myocarditis, pericarditis, vasculitis; nervous system: meningitis, encephalitis, myelitis and demyelination, myasthenic syndrome/myasthenia gravis (including exacerbation), Guillain-Barré syndrome, nerve paresis, autoimmune neuropathy; ocular: uveitis, iritis, and other ocular inflammatory toxicities can occur; gastrointestinal: pancreatitis to include increases in serum amylase and lipase levels, gastritis, duodenitis; musculoskeletal and connective tissue: myositis/polymyositis, rhabdomyolysis, and associated sequelae including renal failure, arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica; endocrine: hypoparathyroidism; other (hematologic/immune): hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), systemic inflammatory response syndrome, histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi lymphadenitis), sarcoidosis, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, solid organ transplant rejection.
Some ocular IMAR cases can be associated with retinal detachment. Various grades of visual impairment, including blindness, can occur. If uveitis occurs in combination with other immune-mediated adverse reactions, consider a Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada–like syndrome, which has been observed in patients receiving OPDIVO, as this may require treatment with systemic corticosteroids to reduce the risk of permanent vision loss.
Infusion-Related Reactions
OPDIVO can cause severe infusion-related reactions. Discontinue OPDIVO in patients with severe (Grade 3) or life-threatening (Grade 4) infusion-related reactions. Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion in patients with mild (Grade 1) or moderate (Grade 2) infusion-related reactions. In patients receiving OPDIVO monotherapy as a 60- minute infusion, infusion-related reactions occurred in 6.4% (127/1994) of patients. In a separate trial in which patients received OPDIVO monotherapy as a 60-minute infusion or a 30-minute infusion, infusion-related reactions occurred in 2.2% (8/368) and 2.7% (10/369) of patients, respectively. Additionally, 0.5% (2/368) and 1.4% (5/369) of patients, respectively, experienced adverse reactions within 48 hours of infusion that led to dose delay, permanent discontinuation or withholding of OPDIVO.
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Fatal and other serious complications can occur in patients who receive allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) before or after being treated with OPDIVO. Transplant-related complications include hyperacute graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD), acute GVHD, chronic GVHD, hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) after reduced intensity conditioning, and steroid-requiring febrile syndrome (without an identified infectious cause). These complications may occur despite intervening therapy between OPDIVO and allogeneic HSCT.
Follow patients closely for evidence of transplant-related complications and intervene promptly. Consider the benefit versus risks of treatment with OPDIVO prior to or after an allogeneic HSCT.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action and findings from animal studies, OPDIVO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with OPDIVO and for at least 5 months after the last dose.
Increased Mortality in Patients with Multiple Myeloma when OPDIVO is Added to a Thalidomide Analogue and Dexamethasone
In randomized clinical trials in patients with multiple myeloma, the addition of OPDIVO to a thalidomide analogue plus dexamethasone resulted in increased mortality. Treatment of patients with multiple myeloma with a PD-1 or PD-L1 blocking antibody in combination with a thalidomide analogue plus dexamethasone is not recommended outside of controlled clinical trials.
Lactation
There are no data on the presence of OPDIVO in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 5 months after the last dose.
Serious Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 274, serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients receiving OPDIVO (n=351). The most frequent serious adverse reaction reported in ≥2% of patients receiving OPDIVO was urinary tract infection. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1% of patients; these included events of pneumonitis (0.6%).
Common Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 274, the most common adverse reactions (≥20%) reported in patients receiving OPDIVO (n=351) were rash (36%), fatigue (36%), diarrhea (30%), pruritus (30%), musculoskeletal pain (28%), and urinary tract infection (22%).
Please see US Full Prescribing Information for OPDIVO.
References
1. Drakaki A, Pantuck A, Mhatre SK, et al. “Real-world” outcomes and prognostic indicators among patients with high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 2021;39:76.e15-76.e22.
2. Referenced without permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Bladder Cancer V.2.2022. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2022. All rights reserved. Accessed August 4, 2022. To view the most recent and complete version of the guidelines, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
3. Apolo AB, Msaouel P, Niglio S, et al. Evolving Role of Adjuvant Systemic Therapy for Kidney and Urothelial Cancers. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2022;42:1-16. doi:10.1200/EDBK_350829.
4. Nayan M, Bhindi B, Yu JL, et al. The initiation of a multidisciplinary bladder cancer clinic and the uptake of neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A time-series analysis. Can Urol Assoc J. 2016;10(1-2):25-30.
5. OPDIVO [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company.
6. Bajorin DF, Witjes JA, Gschwend JE, et al. Adjuvant nivolumab versus placebo in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(22):2102-2114.
7. Bajorin DF, Witjes JA, Gschwend JE, et al. First results from the phase 3 CheckMate 274 trial of adjuvant nivolumab versus placebo in patients who underwent radical surgery for high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. Oral presentation at ASCO GU 2021. Abstract 391.
8. Bajorin DF, Witjes JA, Gschwend JE, et al. Adjuvant nivolumab versus placebo in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(22):2102-2114 [supplementary appendix].
9. American Cancer Society. Bladder cancer early detection, diagnosis, and staging. Accessed August 5, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/CRC/PDF/Public/8559.00.pdf.
10. Data on file. NIVO 639. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2021.
11. Witjes JA, Bajorin DF, Galsky MD, et al. Results for patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer in the CheckMate 274 trial. Poster presentation at ASCO 2022. Abstract 4585.
12. Galsky MD, Witjes JA, Gschwend JE, et al. Disease-free survival with longer follow-up from the phase 3 CheckMate 274 trial of adjuvant nivolumab in patients who underwent surgery for high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. Oral presentation at the American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting 2022. Abstract 22-3807.
© 2022 Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. OPDIVO® and the related logos are trademarks of Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. 1506-US-2200368 8/22
Late Breaking Abstract – ESMO 2022: PADCEV® plus KEYTRUDA® in Previously Untreated Cisplatin-Ineligible Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Cancer
SUMMARY: The American Cancer Society estimates that in the United States for 2022, about 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed and approximately 17,100 patients will die of the disease. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men, but it is less common in women. A third of the patients initially present with locally invasive or metastatic disease. Patients with urothelial carcinoma are currently treated in the first line setting with a Platinum based chemotherapy regimen, and a checkpoint Inhibitor (PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor) in the second line setting. Approximately 50% of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma are ineligible for Cisplatin-based chemotherapy. There is therefore a critical need for effective and tolerable first line treatment options in locally advanced or metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma.
Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv (PADCEV®) is an Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) that targets Nectin-4, a cell adhesion molecule highly expressed in urothelial cancers and other solid tumors. Nectin-4 has been implicated in tumor cell growth and proliferation. Following binding to Nectin-4 on the cell surface, Enfortumab vedotin becomes internalized and is processed by lysosomes, with the liberation of its cytotoxic payload, Monomethyl auristatin E, which in turn disrupts microtubule assembly, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Enfortumab vedotin resulted in significantly longer Overall Survival, Progression Free Survival, and a higher Overall Response Rate, than standard chemotherapy, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, who had previously received Platinum-based treatment and a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor. Preclinical studies with Enfortumab vedotin have shown hallmarks of immune cell death potentially augmented by PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and the rationale for this clinical trial was based on results from a previous cohort study.
Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA®) is a fully humanized, Immunoglobulin G4, anti-PD-1, monoclonal antibody, that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. By doing so, it unleashes the tumor-specific effector T cells, and is thereby able to undo PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response. Pembrolizumab is the first agent to improve Overall Survival over chemotherapy, in the second line setting, for patients with recurrent, advanced urothelial carcinoma, and a significant proportion of patients who respond, have very durable responses.
EV-103 is a clinical trial conducted to examine the safety and efficacy of Enfortumab vedotin given as monotherapy, and in combination with other anticancer therapies, as first line and second line treatment, for patients with urothelial cancer. This study was conducted in multiple parts for both locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer and muscle invasive bladder cancer.
EV-103/KEYNOTE-869 Cohort K is a randomized cohort investigating Enfortumab vedotin alone or in combination with Pembrolizumab as first line treatment in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer, who are ineligible to receive Cisplatin-based chemotherapy. In this Phase Ib/II randomized study, 149 eligible patients (N=149) were randomly assigned to receive a combination of Enfortumab vedotin 1.25 mg/kg given intravenously on days 1 and 8, and Pembrolizumab 200 mg given intravenously on day 1, every 21 days (N=76) or Enfortumab vedotin monotherapy given on the same schedule (N=73). Ineligibility for Cisplatin-based chemotherapy could be due to at least one of the following: Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) less than 60 mL/min, ECOG Performance Status of 2, Grade 2 or more hearing loss, or New York Heart Association Class III heart failure. No prior systemic treatment for locally advanced or metastatic disease, and adjuvant/neoadjuvant Platinum-based therapy within 12 months prior to randomization, were allowed. The Primary endpoint was confirmed Objective Response Rate (ORR) by BICR (Blinded Independent Central Review). Secondary endpoints included Duration of Response (DOR), Safety, Progression Free Survival (PFS) and Overall Survival (OS).
At a median follow up of 14.2 months, the confirmed Objective Response Rate was 64.5% with the Enfortumab vedotin and Pembrolizumab combination, with 10.5% of patients experiencing a Complete Response and 53.9% of patients experiencing a Partial Response. The median Duration of Response was not reached. The most common Treatment-Related Adverse Events (TRAEs) were peripheral sensory neuropathy (55.6%), fatigue (51.1%), and alopecia (48.9%).
It was concluded that in Cisplatin-ineligible patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer, treatment with Enfortumab vedotin and Pembrolizumab combination in chemo naïve patients, resulted in high Overall Response Rate, along with a safety profile that was tolerable. The authors added that Antibody-Drug Conjugates have the potential to make a greater impact in treating bladder cancer, especially in combination with checkpoint inhibitors, as shown in this trial and these data support ongoing investigations of first line Enfortumab vedotin and Pembrolizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer.
Study EV-103 Cohort K: Antitumor activity of enfortumab vedotin (EV) monotherapy or in combination with pembrolizumab (P) in previously untreated cisplatin-ineligible patients (pts) with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer (la/mUC). Rosenberg JE, Milowsky M, Ramamurthy C, et al. Annals of Oncology (2022) 33 (suppl_7): S808-S869. 10.1016/annonc/annonc1089. LBA73
Long Term Disease Free Survival Benefits with Adjuvant OPDIVO® in Urothelial Carcinoma
SUMMARY: The American Cancer Society estimates that in the United States for 2022, about 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed and approximately 17,100 patients will die of the disease. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men, but it is less common in women. A third of the patients initially present with locally invasive disease. Even though radical cystectomy is considered the standard of care for patients with localized Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC), two large randomized trials and two meta-analyses have shown greater survival benefit with neoadjuvant Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy for patients with MIBC, compared to surgery alone. However, not all patients with MIBC benefit from neoadjuvant Cisplatin based therapy, with only 25-50% attaining a pathologic response. More than 50% of patients with MIBC or regional lymph node involvement will develop metastatic disease following radical cystectomy. There is presently no clear consensus with regards to the routine use of adjuvant Cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Further, not all patients are eligible for adjuvant or neoadjuvant Cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
OPDIVO®(Nivolumab) is a fully human, immunoglobulin G4 monoclonal antibody that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2. Blocking the Immune checkpoint proteins unleashes the T cells, resulting in T cell proliferation, activation and a therapeutic response. OPDIVO® has been shown to have antitumor activity in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma who had previously received platinum treatment, and is presently approved by the FDA for this patient group, as well as adjuvant treatment of patients with urothelial carcinoma who are at high risk of recurrence after undergoing radical resection.
CheckMate 274 is a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, Phase III trial conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of adjuvant OPDIVO®, as compared with placebo, in patients with muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma following radical surgery (with or without previous neoadjuvant Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy). A total of 709 patients with muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma who had undergone radical surgery were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive either OPDIVO® 240 mg as a 30-minute IV infusion (N=353) or placebo (N=356), every 2 weeks for up to 1 year. To be eligible, patients must have had radical surgery (R0, with negative surgical margins), with or without neoadjuvant Cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Patients must have had pathological evidence of urothelial carcinoma (originating in the bladder, ureter or renal pelvis) with a high risk of recurrence defined as follows: pathological stage of pT3, pT4a, or pN+ and patients not eligible for or declined adjuvant Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy, patients who had not received neoadjuvant Cisplatin-based chemotherapy, and pathological stage of ypT2 to ypT4a or ypN+ for patients who received neoadjuvant Cisplatin. The mean age was 65.3 years and both treatment groups were well balanced. Approximately 40% of patients in both treatment groups had PD-L1 expression of 1% or more and 43% of patients had received previous neoadjuvant Cisplatin therapy. The two Primary endpoints were Disease Free Survival (DFS) among all the patients, and among patients with a tumor Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression level of 1% or more. Secondary endpoints included NonUrothelial Tract Recurrence-Free Survival (NUTRFS) and Distant Metastasis-Free Survival (DMFS), Overall Survival and Safety.
The authors in this publication reported the DFS outcomes, with 5 additional months of follow up, in all randomized patients. Patients with high-risk, muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma continued to experience clinically meaningful improvements in Disease Free Survival (DFS), with a median DFS of 22.0 months among those receiving OPDIVO® (95% CI, 17.7-36.9) compared with 10.9 months (95% CI, 8.3-14.0) among those receiving placebo (HR=0.70; 95% CI, 0.57-0.85). The DFS probability at 12 months was 63.5% with OPDIVO® versus 46.9% with placebo. The DFS benefit was even more significant in patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or more and was Not Reached in the OPDIVO® group versus 8.4 months in the placebo group (HR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.38-0.75). The DFS probability at 12 months was 67.6% with OPDIVO® versus 46.3% with placebo. The DFS benefits was observed with OPDIVO® among most subgroups analyzed, including age, sex, ECOG PS, nodal status and use of prior Cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
NonUrothelial Tract Recurrence-Free Survival (NUTRFS) and Distant Metastasis-Free Survival (DMFS) were also improved with OPDIVO® when compared to placebo, both in all randomized patients, as well as patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or more.
It was concluded that with longer follow up, OPDIVO® continued to show clinically meaningful improvement in Disease Free Survival among patients with high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma, when compared to placebo, both in all randomized patients, as well as patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or more. OPDIVO® also improved NonUrothelial Tract Recurrence-Free Survival (NUTRFS) and Distant Metastasis-Free Survival when compared to Placebo. The authors added that these results support adjuvant OPDIVO® as a Standard of Care for high risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma patients after radical surgery.
Galsky M, Witjes JA, Gschwend JE, et al. Disease-free survival with longer follow-up from the CheckMate 274 trial of adjuvant nivolumab in patients after surgery for high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. J Urol. 2022;207(suppl 5):e183. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000002536.01
